THE AVIATION SUPERSTORE FOR ALL YOUR AIRCRAFT & PILOT NEEDS | +61 (1800) 953522
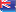
Macchi Castoli M.C. 72 Model
$331.05/Each
Price Includes GST
Part# 13-11028
MFR Model# KMC72TE
MFR Model# KMC72TE
Overview
|
The Macchi M.C. 72 is an experimental seaplane designed and built by Macchi Aeronautica, an aircraft company. Macchi M.C. 72 was built in 1931, and was planned to compete in the final Schneider Trophy race. Unfortunately, the aircraft was unable to compete due to engine problems. Instead of halting the development program, Macchi continued work on the M.C. 72. The Macchi M.C. 72 suffered many mechanical defects, as well as the loss of two test pilots who died trying to coax world class speed out of the aircraft. Macchi M.C. 72s design was unique with a fuselage partly metal to the cockpit and wood monocoque bolted to the front tubular portion by four bolts. The final design of M.C. 72 used a double, counter-rotating fixed-pitch propeller powered by a modified Fiat AS-6 engine generating 2,500 to 3,100 horse power. The engines were overhauled in preparation for a record attempt after the M.C. 72s 35th flight. It set a new world speed record on April 1933 of 682 km/h and was piloted by Warrant Officer Francesco Agello. Further development continued as the M.C. 72s designers thought they could break the 700 km/h record and this feat was achieved on October 23, 1934, when Warrant Officer Francesco Agello piloted the plane for an average speed of 709 km/h over three passes. As of 2006, the record remains the fastest speed ever attained by a piston engine seaplane. Though after the aircrafts success, it was never flown again. Theres one M.C. 72 currently on display at the Vignia de Valle Aircraft Museum, which is near Rome. |
Q&A
Please note, Aircraft Spruce Australia's personnel are not certified aircraft mechanics and can only provide general support and ideas, which should not be relied upon or implemented in lieu of consulting an A&P or other qualified technician. Aircraft Spruce Australia assumes no responsibility or liability for any issue or problem which may arise from any repair, modification or other work done from this knowledge base. Any product eligibility information provided here is based on general application guides and we recommend always referring to your specific aircraft parts manual, the parts manufacturer or consulting with a qualified mechanic.

 Aircraft Spruce Australia
Aircraft Spruce Australia














